Differences between the versions
Differences between the GAEB formats
With the introduction of GAEB DA XML in version 3.3, electronic data exchange via GAEB XML in the construction industry is becoming increasingly important for all partners involved in construction. In this document we would like to briefly show the differences between the current GAEB formats.
While the GAEB 90 format was line-oriented, GAEB 2000 and GAEB DA XML work with key words. Due to this completely different technology, trying to describe the differences between the GAEB file formats would be an almost impossible task.
In principle, it should not matter to you as a user, because the important thing is that GAEB-Online 2025 can work with the different GAEB file formats via the GAEB interface. However, so that you can still recognise the difference, we show on this page the different representation of a simple item as GAEB 90, GAEB 2000 and GAEB DA XML.
Position on paper
First we look at a simple position as you would see it legibly on a paper printout.

The item has a one-line short text, a long text, the quantity 100.00 and the unit m3.
Position as GAEB 90 file
Here is an example of how this item is represented electronically in file form in GAEB 90 format.

In GAEB 90 format, our position is actually still quite legible. The short text always starts with 25 at the beginning of the line.
Position as GAEB 2000 file
Now the example of how the same position is electronically represented in file form in GAEB 2000 format.
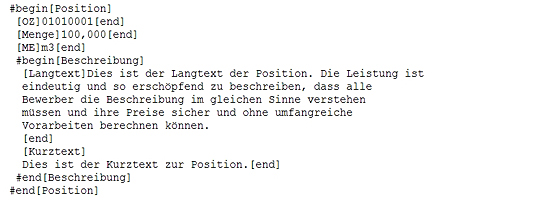
Our position can still be recognised in the GAEB 2000 format. It is remarkable that there is no line-by-line structure as in GAEB 90 and that the elements such as the short text start with the keyword [short text].
Position as GAEB DA XML file
And last but not least, the example of how this item is electronically represented in file form in GAEB DA XML format.

In the GAEB DA XML format it is already very difficult for the human eye to recognise our position. Here, too, there are keywords for the individual elements, the short text begins with the keyword < TextOutlTxt >. In order to avoid confusion, this example does not include possible formatting of the long text, such as colours, bold, italics, etc.
Format texts and images
GAEB 2000 and GAEB DA XML also have the ability to transfer formatting in long texts (colours, bold, italics, bullet points, tables, ...). Graphics or images can also be transferred with the long text. This is not possible with GAEB 90.
Further differences between the GAEB formats
Besides the different representation, there are also general differences between the GAEB formats. These are shown in the following table.
| Element | GAEB DA XML | GAEB 2000 | GAEB 90 |
| Length OZ (item number) | 14 digits | 14 digits | 9 digits |
| Lines long text | unlimited | unlimited | 999 lines |
| Formatted long text | Yes | Yes | No |
| Graphics in long text | Yes | Yes | No |
| Tables in text | Yes | Yes | No |
| Price shares | 6 | 6 | 4 |
| Outline levels | 5 | 5 | 4 |
The table clearly shows that with the new GAEB DA XML considerably more information can be transmitted in terms of content. Formatting and tables in the long text, or even sketches and pictures in the long text contribute to the fact that descriptions are often much easier to read and thus easier to understand for bidders. This often eliminates ambiguities, which always has an influence on prices.
GAEB file formats and file extensions
Which GAEB files are available: The following table shows the GAEB exchange phases and formats supported by our solution GAEB-Online 2025.
| Data exchange | GAEB DA XML | GAEB 2000 | GAEB 90 |
| Universal LV data | X80 | - | - |
| Service description | X81 | P81 | D81 |
| Cost estimate | X82 | P82 | D82 |
| Request for quotation | X83 | P83 | D83 |
| Bid submission | X84 | P84 | D84 |
| Secondary bid | X85 | P85 | D85 |
| Placing of order | X86 | P86 | D86 |